How to Estimate Your Homeowners Insurance (Without a Calculator)
13 Min Read | May 1, 2025

Key Takeaways
- Home insurance premiums are based on several factors like replacement cost, location, age of the home, coverage levels and personal claims history.
- Millions of homeowners are underinsured because they don't know how to calculate the right amount of coverage, often opting for the cheapest policy.
- To determine your coverage needs, we don’t use a tool or widget here. Instead, we’ll walk you through how much coverage you need—on your terms—breaking down the cost to rebuild your home, replace personal property, and protect your assets from potential lawsuits.
Let’s be real: Most “home insurance cost calculators” give you vague estimates based on generic info. And that’s the last thing you want when it comes to protecting your biggest investment.
Instead of plugging numbers into a random form, we’ll show you how to estimate your own homeowners insurance costs the right way—based on your actual home, belongings and financial situation.
Having the right amount of homeowners insurance is crucial to protecting your home and your money. After all, your home is your biggest investment, and a lot can go wrong that could potentially devastate your financial goals.
Here's A Tip
Don’t have a calculator? You don’t need one. Most home insurance calculators are just basic estimators based on generic data. We’ll show you how to figure out what you actually need—step by step—so you’re not underinsured or overpaying.
We’ll start by explaining how insurance companies calculate homeowners premiums and then show you how to come up with your own estimate for how much coverage you need. (And in case you’re just starting to research home insurance, check out our handy Homeowners Insurance Guide.) Even if you flunked math in school (or just didn’t do so well), don’t worry—you can still figure out what you need.
- How Is Homeowners Insurance Cost Calculated?
- Factors That Affect Homeowners Insurance Premiums
- Homeowners Insurance Cost Calculator: How to Estimate Your Needs
- Calculating Your Home’s Replacement Cost
- Four Different Types of Replacement Cost Coverage
- Calculating the Replacement Cost of Personal Property
- Calculating Your At-Risk Assets
- Why Is My Homeowners Insurance So Expensive?
- Getting the Right Coverage
How Is Homeowners Insurance Cost Calculated?
The homeowners insurance secret sauce is complex. But it’s not impossible to understand.
First, keep in mind that insurance companies are ultimately in the business of making money (duh). No matter how noble their other intentions might be, no company can lose money for long and stay in business. This means the price they charge is a balancing act.
Charging too little could put them out of business. Charging too much will potentially push customers away.
So, what do they do? Well, in the era of Big Data, they turn to the numbers. When analyzing risk, insurers focus on two main factors: 1) where you live and 2) how risky you are. They look at how likely you are to file claims and how much those claims will cost them.
Here’s how insurers generally figure out what to charge for homeowners
insurance premiums. (Have your calculator app handy—we’re about to do some insurance math.)
1. Pure Premium
Do you have the right insurance coverage? You could be saving hundreds! Connect with an insurance pro today!
The pure premium is one of the first numbers insurance companies calculate for groups of similar homeowners (for instance, homeowners in Los Angeles). One of the factors that goes into the pure premium math is dividing the group’s total property losses by their total property value. To get a realistic idea of risk, companies typically consider data from at least the past five years for the group.1 So if the properties were valued at $200 million and the losses totaled $10 million, their losses would be 5%, or five cents for every dollar of property value.
2. Expense Ratio
Once they have the pure premium, insurers find the expense ratio (basically the insurance company’s operating expenses plus desired profit). This is usually a percentage and includes things like taxes, underwriting, administrative costs, marketing and commissions.
3. Premium Price
Insurers then take the pure premium and the expense ratio, plug them into their fancy insurance calculators—and out pops what’s called the gross premium. (We have to agree with the name.) This is what you end up paying.
But wait, there’s more . . .
There are a few other things home insurance companies factor in when calculating premiums.
Replacement Cost
Your replacement cost—how much it would cost to rebuild your house—is a big part of your premium. (We’ll show you how to calculate it in a second.)
Location and Age of Your Home
Another huge factor is where your home is located. If you’re in a flood zone, live in a high-crime area, or your home is older (so there’s a greater chance it will need repairs)—you can expect higher premiums. Basically, higher risk means higher cost. Kinda makes sense . . .
Here's A Tip
Check if your provider offers a discount for safety enhancements. Installing a burglar alarm and deadbolt locks would boost your security and could lower your premium too.
Level of Coverage and Deductible
Your premium is also based on how much coverage you choose and the size of your deductible. A higher deductible will mean a lower monthly rate because you’ll pay more out of pocket before the insurance company has to cover a claim. But before you raise your deductible, be sure you have a full emergency fund to cover the new amount.
Construction Type
We’re talking about what your house is made of—brick, wood, etc. A home built with more durable materials are less likely to be damaged—so insurers often offer lower premiums to reflect that reduced risk..
Personal Claims History
If you have a long history of filing claims for every little thing, an insurer is going to take that into account. Filing claims on small repairs will only cost you more in the long run. In fact, it could increase your premium even if your neighbors file a lot of claims. (That might not seem fair, but it’s a factor.)
Your Home’s Square Footage
The larger the home, the more expensive it is to insure. Keep that in mind before you add that epic kitchen bump-out or expand the laundry room!
How Many Live There
If you, your spouse, your children and your entire extended family are all living under the same roof . . . we hope you’ve got a huge refrigerator! But seriously, with that many people sharing space, you’ll pay more for liability coverage because there’s a higher likelihood of incidents.
Insurance companies will also look at things like the type of roof you have, how close you are to resources like fire and police stations, whether you have dogs (including the breed), your credit score and the kind of security and fire alarm systems you have.
Homeowners Insurance Cost Calculator: How to Estimate Your Needs
Now that we’ve covered how insurance companies do their calculations, we’re ready to tackle your coverage estimates. While we can’t help you calculate your exact premium (since insurance math is a closely guarded secret), we can still help you estimate how much coverage you need. When calculating your homeowners insurance needs, start with these three questions:
- How much would it cost to totally rebuild my home at current construction costs?
- How much would it cost to replace my personal belongings?
- If someone sued me for liability and won, what personal assets would be at risk?
You should also consider whether you live in an area that’s at higher risk for extreme weather. Think about natural disasters like floods, earthquakes and hurricanes. While a standard homeowners policy covers a lot of different events, flooding and hurricanes are two things it won’t cover.
The answers to these questions will tell you how much homeowners insurance to get in these three main areas:
- Dwelling coverage, which protects your house
- Personal property insurance, which covers your personal belongings
- Liability coverage, which handles legal bills if you’re sued over an accident on your property
Here's A Tip
Live in an area prone to floods, earthquakes or hurricanes? You may need extra policies, since standard homeowners insurance won’t cover those disasters.
Calculating Your Home’s Replacement Cost
Thankfully, there’s a simple way to calculate your home’s replacement cost. And this number will tell you exactly how much dwelling coverage to get.
Multiply your home’s square footage by your local area’s average cost to rebuild per square foot. Let’s say your house is 3,000 square feet, and the average construction cost in your area is $100 per square foot. So, you multiply 3,000 by $100 and get $300,000. That’s the amount of dwelling coverage you should get.
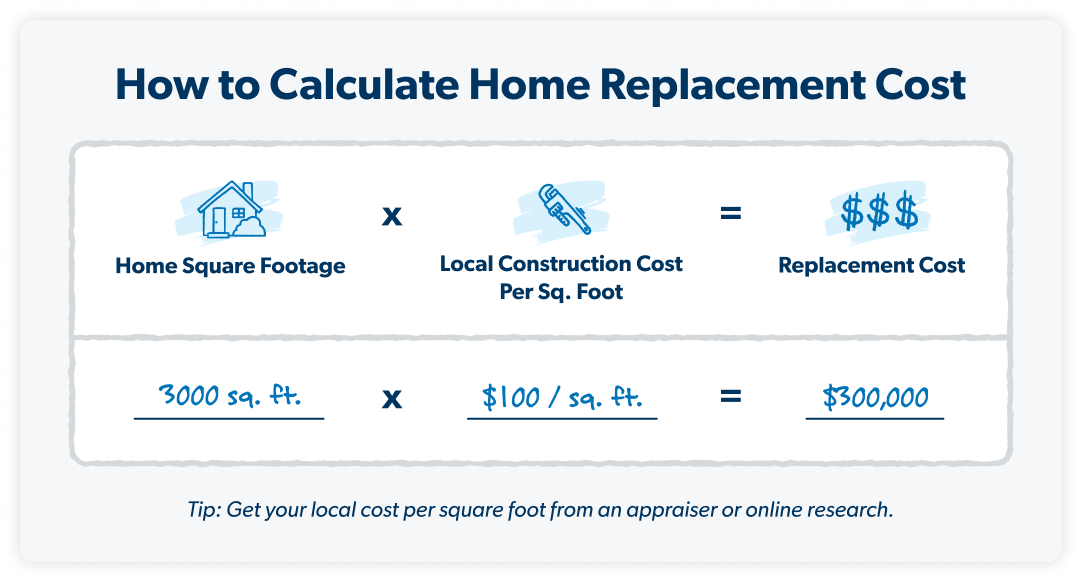
You can find the average construction cost in your area by doing some research online or hiring an appraiser. You can also work with an insurance agent to get this number. And remember that your replacement cost is different from your home’s market value or how much you paid for it. You’re looking for how much it would be to rebuild.
Four Types of Replacement Cost Coverage
Now that you have your replacement cost pinned down, you have four coverage options to choose from.
Actual Cash Value
An actual cash value (ACV) policy will cover your house and belongings minus depreciation. So if you experience a house fire, your insurer will only pay for what the buildings on your property were worth when they burned down—not when you first bought them.
Replacement Cost
Replacement cost coverage is an extra layer of protection since it doesn’t factor in depreciation. It pays to repair or replace your house up to its current value (with some limits). For instance, if you have a $300,000 dwelling coverage limit and the rebuild costs $350,000, you’ll have to pay $50,000 plus your deductible. But if the rebuild only costs $290,000, your insurance will cover it—minus your deductible.
Extended Replacement Cost
Another option is extended replacement cost coverage. This will pay for the replacement value of your home (up to the coverage limit) but with an extra percentage of the coverage limit thrown in. It’s more expensive than basic replacement cost coverage but can come in handy if you live in an area where construction costs are rising quickly (which seems to be nationwide in 2025).
Guaranteed Replacement Cost
Guaranteed replacement cost gives you even more coverage, but you’ll pay more for it. It pays for the full replacement cost of your home and doesn’t factor in depreciation or dwelling coverage limits. So, if it costs $350,000, $400,000 or $500,000 to rebuild your home, that’s what the insurer will pay. No ifs, ands or buts about it.
Calculating the Replacement Cost of Personal Property
Next, you’ll need to figure out how much it would cost to replace your stuff. The best way to do this is by creating an inventory of everything you own. This might sound hard, but we’ll give you a few tips on how to quickly check this off your list.
- Write it all down. Pick a weekend when you’ll have some larger blocks of time (in other words, Thanksgiving is not a good time to bite this off). Then go through your house and garage and write down everything you own and how much it’s worth. Create a spreadsheet where you can total everything up. Also, since depreciation is a factor, estimate how much your stuff is worth now—not what you paid for it 20 years ago.
- Make a digital record. Take photos and videos so you have an even more thorough record. And note more expensive items like jewelry or art, since there is a limit to what the insurance company will pay. You might need extra coverage for pricier items.
- Keep it safe. Finally, keep the spreadsheet and documents in a place where they won’t be lost if there’s a house fire.
Most people undervalue their belongings, so creating this inventory is crucial. When you actually add everything up, you might be surprised how much it’s all worth (and how much you still need to organize or get rid of!).
It’s also a good idea to send your inventory to your insurance company so they have the proof on file. This will help a lot when it comes time to file a claim. And don’t forget to set a reminder to update your inventory every year to make sure it’s current.
Now that you know how much your belongings are worth, you can figure out how much coverage to get. Usually, your policy limit for personal property replacement is around 50% to 75% of your dwelling coverage. But you can increase this limit if you need to.
Calculating Your At-Risk Assets
The third and final calculation you should make is the total value of your assets that would be at risk if you lost a lawsuit. This number will determine how much personal liability insurance you should have. If you don’t have personal liability insurance, many of your assets would be at risk in a legal battle. These assets include:
- Your vehicles (if they’re titled in your name)
- Future wages
- Savings
- Some investments, including real estate
- Personal belongings
- Boats
- Business assets
Depending on where you live, some assets may be protected and won’t be subject to seizure in a lawsuit. These include things like:
- IRA accounts
- Annuities
- Social Security benefits
- Equity in your home
- Employer-sponsored 401(k)s
Create a separate inventory of assets that would be at risk in a lawsuit. Once you have this number, you’ll have a better idea of how much liability coverage you need. You can purchase liability starting from $100,000 all the way up to $1 million. If you need more, you may want to look into getting umbrella insurance for an even stronger defense.
Why Is My Homeowners Insurance So Expensive?
The average cost of homeowners insurance is $1,411 for an annual premium (but that can vary a lot based on your home’s location, value and coverage amount).2 That works out to around $117 a month. If you’re paying more, you might be wondering why. While your insurance company won’t tell you (the software and data that each company uses is actually a heavily guarded secret), there are a few reasons you could be paying higher premiums. It could be based on:
- Where you live
- Your home’s value
- Your deductible
(It’s always good to check the details of your current homeowners insurance by looking at your insurance declaration page. That’s just a fancy term for a summary of your insurance policy. It outlines the who, what, and how much of your insurance policy.)
While those are factors you can (kind of) control, there are other industry-related reasons why you’ve noticed your insurance rates getting higher. Rates nationwide have been rising steadily since the Great Recession of 2007–2008, and premiums rose even more sharply—20%—from 2020 to 2023.3 Several main factors are driving the premium surge: rising property values, increased natural disasters and global supply chain shortages.
At the end of the day, insurance is a tricky business, and you’re not always going to know why your rate is higher. That’s why it’s important to know how to calculate the right amount of insurance you need—so you’re not overpaying. You can also work with an experienced, independent insurance agent to shop around and compare rates for the coverage that fits your situation.
Getting the Right Coverage
There’s a lot that goes into how homeowners insurance is calculated. It’s complicated!
If you’re tired of wondering how it all works or how to get the right coverage, we recommend working with a Ramsey-vetted independent insurance agent.
They’re RamseyTrusted® and can look at your situation to help you find the best coverage at the best price.
When it comes to insuring your biggest investment, the last thing you want is to play guessing games with your coverage. By working with a RamseyTrusted pro, you’ll have peace of mind knowing that your home and belongings are actually covered if something ever happens.
Next Steps
- Check out our Homeowners Insurance Guide for a thorough breakdown of every detail of your coverage needs.
- Calculate how much homeowners insurance you need.
- Find out if you need any extra insurance, like flood insurance, hurricane insurance or earthquake insurance.
- If you already have homeowners insurance, shop around and see if changing carriers or deductibles could save you money.
- Estimate how much your monthly premium will cost.
- Get in touch with a RamseyTrusted insurance pro who can do the heavy lifting for you (like looking into bundling options) and help you figure out the right coverage for your home.
-
What is a homeowners insurance calculator?
-
Most homeowners insurance calculators are just basic estimators based on generic data. You don’t need one to get a basic sense of how much coverage to buy. It’s an estimate you can easily do for yourself.
-
How is homeowners insurance calculated?
-
Insurance companies base your premium on several risk factors like location, home value and rebuilding cost, your claims history, whether you have things like swimming pools or risky dog breeds for pets, the construction type and age of your home, and even (in some states) your credit score. As far as the actual math they use to put that all together? They keep their formula top secret.
-
How much homeowners insurance do I need?
-
That depends on a few things. At the most basic level, the key factors are dwelling, personal property and liability coverage. You add those together to get your total coverage amount.
-
What affects homeowners insurance cost?
-
A whole lot of things can affect your cost. There’s pure premium, the insurance company’s own anticipated expenses to insure you, the location and age of your home, your coverage amount, your deductible, your home’s construction materials, your personal claims history, and more.



